Código aquí
package ejercicio;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public void quickSort(Vehiculo vector[]) {
int n = vector.length;
quicksort(vector, 0, n - 1);
}
private void quicksort(Vehiculo a[], int primero, int ultimo) {
int i, j, central;
Vehiculo pivote;
central = (primero + ultimo) / 2;
pivote = a[central];
i = primero;
j = ultimo;
do {
while (a[i].compareTo(pivote) < 0) {
i++;
}
while (a[j].compareTo(pivote) > 0) {
j--;
}
if (i <= j) {
Vehiculo aux = a[i]; //intercambio
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = aux;
i++;
j--;
}
} while (i <= j);
if (primero < j) {
quicksort(a, primero, j); // mismo proceso con sublista izqda
}
if (i < ultimo) {
quicksort(a, i, ultimo); // mismo proceso con sublista drcha
}
}
public void listar(Vehiculo arreglo[]) {
int pos = arreglo.length;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
System.out.println((i + 1) + " : " + arreglo[i].toString());
}
System.out.println(".........................................................................");
}
public int busquedaLineal(Vehiculo[] vector, Vehiculo dato) {
int n = vector.length;
int pos = -1;
for (int i = 0; ((i < n) && (pos == -1)); i++) {
if (vector[i].compareTo(dato) == 0) {
pos = i;
}
}
return pos;
}
/**
*
* @param vector
* @param dato
* @return
*/
public int busquedaBinaria(Vehiculo[] vector, Vehiculo dato) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
metodo.quickSort(vector);
int n = vector.length;
int izq = 0;
int der = n - 1;
int centro = (izq + der) / 2;
while ((izq <= der) && (!(vector[centro].compareTo(dato) == 0))) {
if (dato.compareTo(vector[centro]) < 0) {
der = centro - 1;
} else {
izq = centro + 1;
}
centro = (izq + der) / 2;
}
if (izq > der) {
return -1;
} else {
return centro;
}
}
public int busquedaLinealRec(Vehiculo[] vector, Vehiculo dato) {
int n = vector.length;
int i = this.busquedaLinealRecursiva(vector, dato, n - 1, 0);
return i;
}
private int busquedaLinealRecursiva(Vehiculo a[], Vehiculo clave, int n, int i) {
if (i == n + 1) {
return -1;
} else {
if (a[i].compareTo(clave) == 0) {
return i;
} else {
return busquedaLinealRecursiva(a, clave, n, i + 1);
}
}
}
public int busquedaBinariaRec(Vehiculo[] vector, Vehiculo dato) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
metodo.quickSort(vector);
int n = vector.length;
int i = this.busquedaBinariaRecursiva(vector, 0, n - 1, dato);
return i;
}
private int busquedaBinariaRecursiva(Vehiculo vector[], int izq, int der, Vehiculo dato) {
int centro = (izq + der) / 2;
if (izq > der) {
return -1;
} else if (dato.compareTo(vector[centro]) == 0) {
return centro;
} else if (dato.compareTo(vector[centro]) < 0) {
return busquedaBinariaRecursiva(vector, izq, centro - 1, dato);
} else {
return busquedaBinariaRecursiva(vector, centro + 1, der, dato);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
Vehiculo arreglo[] = new Vehiculo[5];
arreglo[0] = new Vehiculo("ada27", 30000D, new Date(112, 10, 12));
arreglo[1] = new Vehiculo("chj5", 27000D, new Date(100, 5, 23));
arreglo[2] = new Vehiculo("cjk77", 40000D, new Date(109, 3, 22));
arreglo[3] = new Vehiculo("bmn90", 35000D, new Date(104, 11, 19));
arreglo[4] = new Vehiculo("asd31", 17000D, new Date(105, 12, 21));
System.out.println("Arreglo con datos");
metodo.listar(arreglo);
Date dato = new Date(104, 11, 19);//podemos validar la fecha revisar entarada antigua
System.out.println("FEcha buscada es "+ dato.toString());
Vehiculo datoVehiculo = new Vehiculo(null, null, dato);
int num;
num = metodo.busquedaLineal(arreglo, datoVehiculo);
// metodo.quickSort(arreglo);
// num = metodo.busquedaLinealRec(arreglo, datoVehiculo);
// num = metodo.busquedaBinaria(arreglo, datoVehiculo);// para que imprima correctamente primero tiene que ordenarlo
// num = metodo.busquedaBinariaRec(arreglo, datoVehiculo);
if(num>0){
System.out.println("El elemneto encontado es "+ arreglo[num].toString());
}else{
System.out.println("Elemento no encontrado");
}
}
}
..........................................................................................................................................................
Clase Vehiculo
package ejercicio;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Vehiculo implements Comparable{
private String placa;
private Double precio;
private Date fechaFabricacion;
public Vehiculo() {
}
public Vehiculo(String placa, Double precio, Date fechaFabricacion) {
this.placa = placa;
this.precio = precio;
this.fechaFabricacion = fechaFabricacion;
}
public String getPlaca() {
return placa;
}
public void setPlaca(String placa) {
this.placa = placa;
}
public void setPrecio(Double precio) {
this.precio = precio;
}
public void setFechaFabricacion(Date fechaFabricacion) {
this.fechaFabricacion = fechaFabricacion;
}
public Double getPrecio() {
return precio;
}
public Date getFechaFabricacion() {
return fechaFabricacion;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
SimpleDateFormat formateador = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
return "{ placa= " + placa + ", precio= " + precio + ", fechaFabricacion=" + formateador.format(fechaFabricacion) + " }";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) { //comparamos String
Vehiculo c = (Vehiculo) o;
int fechaCmp = this.fechaFabricacion.compareTo(c.fechaFabricacion);
return fechaCmp;// aqui solo podemos poner returm placaCmp;
}
}
Captura
viernes, 14 de agosto de 2015
Métodos de ordenación burbuja, selección, inserción, shellSort, MergeSort y QuickSort con objetos en java
Código Aquí
package ejercicio;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void ordSeleccion(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int indiceMenor, i, j, n;
n = vector.length;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
// comienzo de la exploración en índice i
indiceMenor = i;
// j explora la sublista a[i+1]..a[n-1]
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (vector[j].compareTo(vector[indiceMenor]) < 0) {
indiceMenor = j;
}
}
// sitúa el elemento mas pequeño en a[i]
if (i != indiceMenor) {
Vehiculo aux = vector[i];
vector[i] = vector[indiceMenor];
vector[indiceMenor] = aux;
}
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void ordInsercion(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int n = vector.length;
int i, j;
Vehiculo aux;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
/* indice j es para explorar la sublista a[i-1]..a[0] buscando la
posicion correcta del elemento destino*/
j = i;
aux = vector[i];
// se localiza el punto de inserción explorando hacia abajo
while (j > 0 && (aux.compareTo(vector[j - 1]) < 0)) {
// desplazar elementos hacia arriba para hacer espacio
vector[j] = vector[j - 1];
j--;
}
vector[j] = aux;
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void burbuja(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int n = vector.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) // sitúa mínimo de a[i+1]...a[n-1] en a[i]
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if ((vector[i].compareTo(vector[j])) > 0) {
Vehiculo aux = vector[i];
vector[i] = vector[j];
vector[j] = aux;
}
}
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void shellSort(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int intervalo, i, j, k;
int n = vector.length;
intervalo = n / 2;
while (intervalo > 0) {
for (i = intervalo; i < n; i++) {
j = i - intervalo;
while (j >= 0) {
k = j + intervalo;
if (vector[j].compareTo(vector[k]) <= 0) {
j = -1; // par de elementos ordenado
} else {
Vehiculo aux = vector[j];//intercambio
vector[j] = vector[j + 1];
vector[j + 1] = aux;
j -= intervalo;
}
}
}
intervalo = intervalo / 2;
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void quickSort(Vehiculo vector[]) {
int n = vector.length;
quicksort(vector, 0, n - 1);
}
private void quicksort(Vehiculo a[], int primero, int ultimo) {
int i, j, central;
Vehiculo pivote;
central = (primero + ultimo) / 2;
pivote = a[central];
i = primero;
j = ultimo;
do {
while (a[i].compareTo(pivote) < 0) {
i++;
}
while (a[j].compareTo(pivote) > 0) {
j--;
}
if (i <= j) {
Vehiculo aux = a[i]; //intercambio
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = aux;
i++;
j--;
}
} while (i <= j);
if (primero < j) {
quicksort(a, primero, j); // mismo proceso con sublista izqda
}
if (i < ultimo) {
quicksort(a, i, ultimo); // mismo proceso con sublista drcha
}
}
public void mergeSort(Vehiculo arreglo[]) {
int n = arreglo.length;
Vehiculo tmpArray[] = new Vehiculo[n];
mergeSort(arreglo, tmpArray, 0, n - 1);
}
private void mergeSort(Vehiculo a[], Vehiculo b[], int izq, int der) {
int centro;
if (izq < der) {
centro = (izq + der) / 2;
mergeSort(a, b, izq, centro);
mergeSort(a, b, centro + 1, der);
fusion(a, b, izq, centro + 1, der);
}
}
private void fusion(Vehiculo a[], Vehiculo b[], int izq, int centro, int der) {
int finalIzq, nroelem, tmp;
finalIzq = centro - 1;
tmp = izq;
nroelem = der - izq + 1;
while ((izq <= finalIzq) && (centro <= der)) {
if (a[izq].compareTo(a[centro]) < 0) {
b[tmp] = a[izq];
izq++;
} else {
b[tmp] = a[centro];
centro++;
}
tmp++;
}
while (izq <= finalIzq) {
b[tmp] = a[izq];
tmp++;
izq++;
}
while (centro <= der) {
b[tmp] = a[centro];
tmp++;
centro++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= nroelem; i++) {
a[der] = b[der];
der--;
}
}
public void listar(Vehiculo arreglo[]) {
int pos = arreglo.length;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
System.out.println((i + 1) + " : " + arreglo[i].toString());
}
System.out.println(".........................................................................");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
Vehiculo arreglo[] = new Vehiculo[5];
arreglo[0] = new Vehiculo("ada27", 30000D, new Date(1183282843222L));
arreglo[1] = new Vehiculo("chj5", 27000D, new Date(1090092212322L));
arreglo[2] = new Vehiculo("cjk77", 40000D, new Date(1228998294563L));
arreglo[3] = new Vehiculo("bmn90", 35000D, new Date(1393911139902L));
arreglo[4] = new Vehiculo("asd31", 17000D, new Date(1297484838999L));
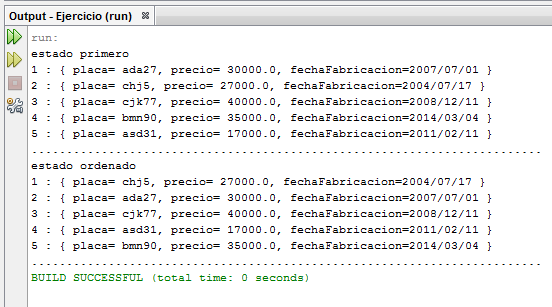
System.out.println("estado primero");
metodo.listar(arreglo);
System.out.println("estado ordenado");
// metodo.burbuja(arreglo);
// metodo.ordInsercion(arreglo);
// metodo.ordSeleccion(arreglo);
// metodo.shellSort(arreglo);
// metodo.mergeSort(arreglo);
metodo.quickSort(arreglo);
metodo.listar(arreglo);
}
}
..........................................................................................................................................................
Clase Vehiculo
package ejercicio;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Vehiculo implements Comparable{
private String placa;
private Double precio;
private Date fechaFabricacion;
public Vehiculo() {
}
public Vehiculo(String placa, Double precio, Date fechaFabricacion) {
this.placa = placa;
this.precio = precio;
this.fechaFabricacion = fechaFabricacion;
}
public String getPlaca() {
return placa;
}
public void setPlaca(String placa) {
this.placa = placa;
}
public void setPrecio(Double precio) {
this.precio = precio;
}
public void setFechaFabricacion(Date fechaFabricacion) {
this.fechaFabricacion = fechaFabricacion;
}
public Double getPrecio() {
return precio;
}
public Date getFechaFabricacion() {
return fechaFabricacion;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
SimpleDateFormat formateador = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
return "{ placa= " + placa + ", precio= " + precio + ", fechaFabricacion=" + formateador.format(fechaFabricacion) + " }";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) { //comparamos String
Vehiculo c = (Vehiculo) o;
int fechaCmp = this.fechaFabricacion.compareTo(c.fechaFabricacion);
return fechaCmp;// aqui solo podemos poner returm placaCmp;
}
}
Captura
package ejercicio;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void ordSeleccion(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int indiceMenor, i, j, n;
n = vector.length;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
// comienzo de la exploración en índice i
indiceMenor = i;
// j explora la sublista a[i+1]..a[n-1]
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (vector[j].compareTo(vector[indiceMenor]) < 0) {
indiceMenor = j;
}
}
// sitúa el elemento mas pequeño en a[i]
if (i != indiceMenor) {
Vehiculo aux = vector[i];
vector[i] = vector[indiceMenor];
vector[indiceMenor] = aux;
}
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void ordInsercion(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int n = vector.length;
int i, j;
Vehiculo aux;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
/* indice j es para explorar la sublista a[i-1]..a[0] buscando la
posicion correcta del elemento destino*/
j = i;
aux = vector[i];
// se localiza el punto de inserción explorando hacia abajo
while (j > 0 && (aux.compareTo(vector[j - 1]) < 0)) {
// desplazar elementos hacia arriba para hacer espacio
vector[j] = vector[j - 1];
j--;
}
vector[j] = aux;
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void burbuja(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int n = vector.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) // sitúa mínimo de a[i+1]...a[n-1] en a[i]
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if ((vector[i].compareTo(vector[j])) > 0) {
Vehiculo aux = vector[i];
vector[i] = vector[j];
vector[j] = aux;
}
}
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void shellSort(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int intervalo, i, j, k;
int n = vector.length;
intervalo = n / 2;
while (intervalo > 0) {
for (i = intervalo; i < n; i++) {
j = i - intervalo;
while (j >= 0) {
k = j + intervalo;
if (vector[j].compareTo(vector[k]) <= 0) {
j = -1; // par de elementos ordenado
} else {
Vehiculo aux = vector[j];//intercambio
vector[j] = vector[j + 1];
vector[j + 1] = aux;
j -= intervalo;
}
}
}
intervalo = intervalo / 2;
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void quickSort(Vehiculo vector[]) {
int n = vector.length;
quicksort(vector, 0, n - 1);
}
private void quicksort(Vehiculo a[], int primero, int ultimo) {
int i, j, central;
Vehiculo pivote;
central = (primero + ultimo) / 2;
pivote = a[central];
i = primero;
j = ultimo;
do {
while (a[i].compareTo(pivote) < 0) {
i++;
}
while (a[j].compareTo(pivote) > 0) {
j--;
}
if (i <= j) {
Vehiculo aux = a[i]; //intercambio
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = aux;
i++;
j--;
}
} while (i <= j);
if (primero < j) {
quicksort(a, primero, j); // mismo proceso con sublista izqda
}
if (i < ultimo) {
quicksort(a, i, ultimo); // mismo proceso con sublista drcha
}
}
public void mergeSort(Vehiculo arreglo[]) {
int n = arreglo.length;
Vehiculo tmpArray[] = new Vehiculo[n];
mergeSort(arreglo, tmpArray, 0, n - 1);
}
private void mergeSort(Vehiculo a[], Vehiculo b[], int izq, int der) {
int centro;
if (izq < der) {
centro = (izq + der) / 2;
mergeSort(a, b, izq, centro);
mergeSort(a, b, centro + 1, der);
fusion(a, b, izq, centro + 1, der);
}
}
private void fusion(Vehiculo a[], Vehiculo b[], int izq, int centro, int der) {
int finalIzq, nroelem, tmp;
finalIzq = centro - 1;
tmp = izq;
nroelem = der - izq + 1;
while ((izq <= finalIzq) && (centro <= der)) {
if (a[izq].compareTo(a[centro]) < 0) {
b[tmp] = a[izq];
izq++;
} else {
b[tmp] = a[centro];
centro++;
}
tmp++;
}
while (izq <= finalIzq) {
b[tmp] = a[izq];
tmp++;
izq++;
}
while (centro <= der) {
b[tmp] = a[centro];
tmp++;
centro++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= nroelem; i++) {
a[der] = b[der];
der--;
}
}
public void listar(Vehiculo arreglo[]) {
int pos = arreglo.length;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
System.out.println((i + 1) + " : " + arreglo[i].toString());
}
System.out.println(".........................................................................");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
Vehiculo arreglo[] = new Vehiculo[5];
arreglo[0] = new Vehiculo("ada27", 30000D, new Date(1183282843222L));
arreglo[1] = new Vehiculo("chj5", 27000D, new Date(1090092212322L));
arreglo[2] = new Vehiculo("cjk77", 40000D, new Date(1228998294563L));
arreglo[3] = new Vehiculo("bmn90", 35000D, new Date(1393911139902L));
arreglo[4] = new Vehiculo("asd31", 17000D, new Date(1297484838999L));
System.out.println("estado primero");
metodo.listar(arreglo);
System.out.println("estado ordenado");
// metodo.burbuja(arreglo);
// metodo.ordInsercion(arreglo);
// metodo.ordSeleccion(arreglo);
// metodo.shellSort(arreglo);
// metodo.mergeSort(arreglo);
metodo.quickSort(arreglo);
metodo.listar(arreglo);
}
}
..........................................................................................................................................................
Clase Vehiculo
package ejercicio;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Vehiculo implements Comparable{
private String placa;
private Double precio;
private Date fechaFabricacion;
public Vehiculo() {
}
public Vehiculo(String placa, Double precio, Date fechaFabricacion) {
this.placa = placa;
this.precio = precio;
this.fechaFabricacion = fechaFabricacion;
}
public String getPlaca() {
return placa;
}
public void setPlaca(String placa) {
this.placa = placa;
}
public void setPrecio(Double precio) {
this.precio = precio;
}
public void setFechaFabricacion(Date fechaFabricacion) {
this.fechaFabricacion = fechaFabricacion;
}
public Double getPrecio() {
return precio;
}
public Date getFechaFabricacion() {
return fechaFabricacion;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
SimpleDateFormat formateador = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
return "{ placa= " + placa + ", precio= " + precio + ", fechaFabricacion=" + formateador.format(fechaFabricacion) + " }";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) { //comparamos String
Vehiculo c = (Vehiculo) o;
int fechaCmp = this.fechaFabricacion.compareTo(c.fechaFabricacion);
return fechaCmp;// aqui solo podemos poner returm placaCmp;
}
}
Captura
Sudoku en java
Código aquí
package ejercicio;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public static final int DIMENSION = 9; // constante
public void imprimir(int[][] tablero) {
for (int i = 0; i < DIMENSION; i++) {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
System.out.println();
}
for (int j = 0; j < DIMENSION; j++) {
if (j % 3 == 0) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.print(tablero[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public boolean resolver(int[][] tablero) {
for (int i = 0; i < DIMENSION; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < DIMENSION; j++) {
if (tablero[i][j] != 0) {
continue;
}
for (int k = 1; k <= 9; k++) {
if (esPosibleInsertar(tablero, i, j, k)) {
tablero[i][j] = k;
boolean b = resolver(tablero);
if (b) {
return true;
}
tablero[i][j] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
}
System.out.println("Encontrada solución:");
imprimir(tablero);
return true;
}
public boolean esPosibleInsertar(int[][] tablero, int i, int j, int valor) {
//Comprueba columna
for (int a = 0; a < DIMENSION; a++) {
if (a != i && tablero[a][j] == valor) {
return false;
}
}
//Comprueba fila
for (int a = 0; a < DIMENSION; a++) {
if (a != j && tablero[i][a] == valor) {
return false;
}
}
//Comprueba cuadardo
int y = (i / 3) * 3;
int x = (j / 3) * 3;
for (int a = 0; a < DIMENSION / 3; a++) {
for (int b = 0; b < DIMENSION / 3; b++) {
if (a != i && b != j && tablero[y + a][x + b] == valor) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public int[][] generarSudoku() {
int[][] sudok = new int[9][9];
for (int i = 0; i < sudok.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sudok[1].length; j++) {
int ale = (int) (Math.random() * 10);
if (ale == 5) {
sudok[i][j] = (int) (Math.random() * 9) + 1;
} else {
sudok[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
return sudok;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio miSudoku = new Ejercicio();
System.out.println("Sudoku generado");
int[][] sudoku = miSudoku.generarSudoku();
miSudoku.imprimir(sudoku);
System.out.println("Aveces puede demorar por el algoritmo entre 3-15 min");
if (!miSudoku.resolver(sudoku)) {
System.out.println("El Sudoku notiene solución");
}
}
}
Captura
package ejercicio;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public static final int DIMENSION = 9; // constante
public void imprimir(int[][] tablero) {
for (int i = 0; i < DIMENSION; i++) {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
System.out.println();
}
for (int j = 0; j < DIMENSION; j++) {
if (j % 3 == 0) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.print(tablero[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public boolean resolver(int[][] tablero) {
for (int i = 0; i < DIMENSION; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < DIMENSION; j++) {
if (tablero[i][j] != 0) {
continue;
}
for (int k = 1; k <= 9; k++) {
if (esPosibleInsertar(tablero, i, j, k)) {
tablero[i][j] = k;
boolean b = resolver(tablero);
if (b) {
return true;
}
tablero[i][j] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
}
System.out.println("Encontrada solución:");
imprimir(tablero);
return true;
}
public boolean esPosibleInsertar(int[][] tablero, int i, int j, int valor) {
//Comprueba columna
for (int a = 0; a < DIMENSION; a++) {
if (a != i && tablero[a][j] == valor) {
return false;
}
}
//Comprueba fila
for (int a = 0; a < DIMENSION; a++) {
if (a != j && tablero[i][a] == valor) {
return false;
}
}
//Comprueba cuadardo
int y = (i / 3) * 3;
int x = (j / 3) * 3;
for (int a = 0; a < DIMENSION / 3; a++) {
for (int b = 0; b < DIMENSION / 3; b++) {
if (a != i && b != j && tablero[y + a][x + b] == valor) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public int[][] generarSudoku() {
int[][] sudok = new int[9][9];
for (int i = 0; i < sudok.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sudok[1].length; j++) {
int ale = (int) (Math.random() * 10);
if (ale == 5) {
sudok[i][j] = (int) (Math.random() * 9) + 1;
} else {
sudok[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
return sudok;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio miSudoku = new Ejercicio();
System.out.println("Sudoku generado");
int[][] sudoku = miSudoku.generarSudoku();
miSudoku.imprimir(sudoku);
System.out.println("Aveces puede demorar por el algoritmo entre 3-15 min");
if (!miSudoku.resolver(sudoku)) {
System.out.println("El Sudoku notiene solución");
}
}
}
Captura
El método generar sudoku es opcional puedes creas una matriz int de 9*9 y meterle datos.
Laberinto en java
Código aquí
package ejercicio;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public void imprime(char[][] lab) {
for (int i = 0; i < lab.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lab[1].length; j++) {
System.out.print(lab[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public char[][] generarLaberinto() {
int n = (int) (Math.random() * 12) + 3;
int m = (int) (Math.random() * 12) + 3;
char[][] lab = new char[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < lab.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lab[1].length; j++) {
int ale = (int) (Math.random() * 2) + 1;
if (ale == 1) {
lab[i][j] = ' ';
} else {
lab[i][j] = '#';
}
}
}
int inicio1 = (int) (Math.random() * lab.length);
int inicio2 = (int) (Math.random() * lab[1].length);
lab[inicio1][inicio2] = '.';
return lab;
}
public boolean resuelveLab(char[][] lab) {
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < lab.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lab[1].length; j++) {
if (lab[i][j] == '.') {
y = i;
x = j;
}
}
}
return resuelve(lab, x, y);
}
private boolean resuelve(char[][] lab, int x, int y) {
lab[y][x] = '.';
if (x == 0 || y == 0 || x == lab[0].length - 1 || y == lab.length - 1) {
System.out.println("Encontrada soluciOn: ");
imprime(lab);
return true;
}
// Arriba
if (lab[y - 1][x] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x, y - 1);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// abajo
if (lab[y + 1][x] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x, y + 1);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// Izquierda
if (lab[y][x - 1] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x - 1, y);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// Derecha
if (lab[y][x + 1] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x + 1, y);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// Este camino no tiene solucion
lab[y][x] = ' ';
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio laberinto = new Ejercicio();
System.out.println("Laberinto generado: ");
char[][] lab = laberinto.generarLaberinto();
laberinto.imprime(lab);
boolean soluc = laberinto.resuelveLab(lab);
if (soluc == false) {
System.out.println("No se encontro solucion");
}
}
}
package ejercicio;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public void imprime(char[][] lab) {
for (int i = 0; i < lab.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lab[1].length; j++) {
System.out.print(lab[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public char[][] generarLaberinto() {
int n = (int) (Math.random() * 12) + 3;
int m = (int) (Math.random() * 12) + 3;
char[][] lab = new char[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < lab.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lab[1].length; j++) {
int ale = (int) (Math.random() * 2) + 1;
if (ale == 1) {
lab[i][j] = ' ';
} else {
lab[i][j] = '#';
}
}
}
int inicio1 = (int) (Math.random() * lab.length);
int inicio2 = (int) (Math.random() * lab[1].length);
lab[inicio1][inicio2] = '.';
return lab;
}
public boolean resuelveLab(char[][] lab) {
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < lab.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lab[1].length; j++) {
if (lab[i][j] == '.') {
y = i;
x = j;
}
}
}
return resuelve(lab, x, y);
}
private boolean resuelve(char[][] lab, int x, int y) {
lab[y][x] = '.';
if (x == 0 || y == 0 || x == lab[0].length - 1 || y == lab.length - 1) {
System.out.println("Encontrada soluciOn: ");
imprime(lab);
return true;
}
// Arriba
if (lab[y - 1][x] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x, y - 1);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// abajo
if (lab[y + 1][x] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x, y + 1);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// Izquierda
if (lab[y][x - 1] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x - 1, y);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// Derecha
if (lab[y][x + 1] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x + 1, y);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// Este camino no tiene solucion
lab[y][x] = ' ';
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio laberinto = new Ejercicio();
System.out.println("Laberinto generado: ");
char[][] lab = laberinto.generarLaberinto();
laberinto.imprime(lab);
boolean soluc = laberinto.resuelveLab(lab);
if (soluc == false) {
System.out.println("No se encontro solucion");
}
}
}
Captura
El punto indica donde comienza para encontrar una salida, el método generar laberinto es opcional puedes tu mandar tu matriz chart de cualquier tamaño.
Validar int , double y Date en java
Código aquí
package ejercicio;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public Integer validarInt() {
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean esEntero = false;
int num = -1;
do {
String cadena = leer.nextLine();
try {
num = Integer.parseInt(cadena);
esEntero = true;
} catch (NumberFormatException nfe) {
System.out.println("Escriba un numero");
}
} while (!esEntero);
return num;
}
public Double validarDouble() {
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean esDouble = false;
double num = -1;
do {
String cadena = leer.nextLine();
try {
num = Double.parseDouble(cadena);
esDouble = true;
} catch (NumberFormatException nfe) {
System.out.println("Escriba un numero");
}
} while (!esDouble);
return num;
}
public Date validarFecha() {
SimpleDateFormat formatoDelTexto = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean esFormato = false;
Date fecha = new Date(0);
do {
String cadena = leer.nextLine();
try {
fecha = formatoDelTexto.parse(cadena);
System.out.println("La fecha que ingreso es " + formatoDelTexto.format(fecha));
esFormato = true;
} catch (ParseException ex) {
// ex.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Escriba la fecha cn el formato yyyy/MM/dd");
}
} while (!esFormato);
return fecha;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
int datoInt = metodo.validarInt();
System.out.println("El numero leido es " + datoInt);
double datoDouble = metodo.validarDouble();
System.out.println("El numero leido es " + datoDouble);
Date datoDate = metodo.validarFecha();
System.out.println("La fecha leida es " + datoDate.toString());
}
}
package ejercicio;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public Integer validarInt() {
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean esEntero = false;
int num = -1;
do {
String cadena = leer.nextLine();
try {
num = Integer.parseInt(cadena);
esEntero = true;
} catch (NumberFormatException nfe) {
System.out.println("Escriba un numero");
}
} while (!esEntero);
return num;
}
public Double validarDouble() {
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean esDouble = false;
double num = -1;
do {
String cadena = leer.nextLine();
try {
num = Double.parseDouble(cadena);
esDouble = true;
} catch (NumberFormatException nfe) {
System.out.println("Escriba un numero");
}
} while (!esDouble);
return num;
}
public Date validarFecha() {
SimpleDateFormat formatoDelTexto = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean esFormato = false;
Date fecha = new Date(0);
do {
String cadena = leer.nextLine();
try {
fecha = formatoDelTexto.parse(cadena);
System.out.println("La fecha que ingreso es " + formatoDelTexto.format(fecha));
esFormato = true;
} catch (ParseException ex) {
// ex.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Escriba la fecha cn el formato yyyy/MM/dd");
}
} while (!esFormato);
return fecha;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
int datoInt = metodo.validarInt();
System.out.println("El numero leido es " + datoInt);
double datoDouble = metodo.validarDouble();
System.out.println("El numero leido es " + datoDouble);
Date datoDate = metodo.validarFecha();
System.out.println("La fecha leida es " + datoDate.toString());
}
}
Captura
Cambio de monedas en java
Código aquí
package ejercicio;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public boolean calcular(int monto, int[] valor, int[] num) {
int cont = dineroTotal(valor, num);
if (cont >= monto) {
int[] cambio = this.cambio(monto, valor, num);
for (int i = 0; i < cambio.length; i++) {
System.out.println(valor[i] + " = " + cambio[i] + " unidad(es)");
}
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
private int[] cambio(int monto, int[] valor, int[] num) {
int[] moneda = new int[valor.length];
for (int i = 0; i < valor.length; i++) {
while (valor[i] <= monto && num[i] > 0) {
moneda[i]++;
num[i]--;
monto = monto - valor[i];
}
}
return moneda;
}
public int dineroTotal(int[] valor, int[] num) {
int cont = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
cont += num[i] * valor[i];
}
return cont;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] moneda = {100, 50, 10, 5, 1};// monedad
int[] cantidadMoneda = {((int) (Math.random() * 100)), (int) (Math.random() * 200),
(int) (Math.random() * 400), (int) (Math.random() * 600), (int) (Math.random() * 1000)};//cantidad de monedas aleatorias
//Quiero en monedas
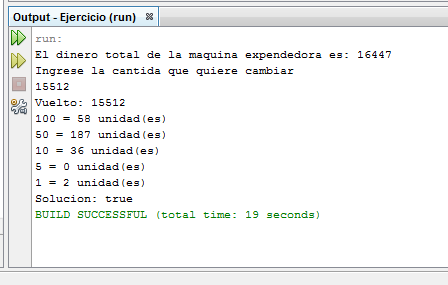
System.out.println("El dinero total de la maquina expendedora es: " + metodo.dineroTotal(moneda, cantidadMoneda));
System.out.println("Ingrese la cantida que quiere cambiar ");
int saldo = leer.nextInt();
System.out.println("Vuelto: " + saldo);
boolean exito = metodo.calcular(saldo, moneda, cantidadMoneda);
System.out.println("Solucion: " + exito);
}
}
package ejercicio;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public boolean calcular(int monto, int[] valor, int[] num) {
int cont = dineroTotal(valor, num);
if (cont >= monto) {
int[] cambio = this.cambio(monto, valor, num);
for (int i = 0; i < cambio.length; i++) {
System.out.println(valor[i] + " = " + cambio[i] + " unidad(es)");
}
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
private int[] cambio(int monto, int[] valor, int[] num) {
int[] moneda = new int[valor.length];
for (int i = 0; i < valor.length; i++) {
while (valor[i] <= monto && num[i] > 0) {
moneda[i]++;
num[i]--;
monto = monto - valor[i];
}
}
return moneda;
}
public int dineroTotal(int[] valor, int[] num) {
int cont = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
cont += num[i] * valor[i];
}
return cont;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] moneda = {100, 50, 10, 5, 1};// monedad
int[] cantidadMoneda = {((int) (Math.random() * 100)), (int) (Math.random() * 200),
(int) (Math.random() * 400), (int) (Math.random() * 600), (int) (Math.random() * 1000)};//cantidad de monedas aleatorias
//Quiero en monedas
System.out.println("El dinero total de la maquina expendedora es: " + metodo.dineroTotal(moneda, cantidadMoneda));
System.out.println("Ingrese la cantida que quiere cambiar ");
int saldo = leer.nextInt();
System.out.println("Vuelto: " + saldo);
boolean exito = metodo.calcular(saldo, moneda, cantidadMoneda);
System.out.println("Solucion: " + exito);
}
}
Corrida
jueves, 13 de agosto de 2015
El salto del caballo en java , backtracking
Codigo aqui
Clase CaballoSaltador
*
* To change this license header, choose License Headers in Project Properties.
* To change this template file, choose Tools | Templates
* and open the template in the editor.
*/
package CaballoSaltador;
/**
*
* @author SaruraiTensai
*/
public class CaballoSaltador {
static final int N = 8;
static final int n = (N + 1);
private int[][] tablero = new int[n][n];
private boolean exito;
private int[][] SALTO = {{2, 1}, {1, 2}, {-1, 2}, {-2, 1},
{-2, -1}, {-1, -2}, {1, -2}, {2, -1}};
private int x0, y0;
// constructor
public CaballoSaltador(int x, int y) throws Exception {
if ((x < 1) || (x > N)
|| (y < 1) || (y > N)) {
throw new Exception("Coordenadas fuera de rango");
}
x0 = x;
y0 = y;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
tablero[i][j] = 0;
}
}
tablero[x0][y0] = 1;
exito = false;
}
public boolean resolverProblema() {
saltoCaballo(x0, y0, 2);
return exito;
}
private void saltoCaballo(int x, int y, int i) {
int nx, ny;
int k;
k = 0; // inicializa el conjunto de posibles movimientos
do {
k++;
nx = x + SALTO[k - 1][0];
ny = y + SALTO[k - 1][1];
// determina si nuevas coordenadas son aceptables
if ((nx >= 1) && (nx <= N) && (ny >= 1) && (ny <= N)
&& (tablero[nx][ny] == 0)) {
tablero[nx][ny] = i; // anota movimiento
if (i < N * N) {
saltoCaballo(nx, ny, i + 1);
// se analiza si se ha completado la solución
if (!exito) { // no se alcanzó la solución
tablero[nx][ny] = 0; // se borra anotación
}
} else {
exito = true; // tablero cubierto
}
}
} while ((k < 8) && !exito);
}
//muestra por pantalla los pasos del caballo
void escribirTablero() {
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
System.out.print(tablero[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Clase CaballoSaltador
*
* To change this license header, choose License Headers in Project Properties.
* To change this template file, choose Tools | Templates
* and open the template in the editor.
*/
package CaballoSaltador;
/**
*
* @author SaruraiTensai
*/
public class CaballoSaltador {
static final int N = 8;
static final int n = (N + 1);
private int[][] tablero = new int[n][n];
private boolean exito;
private int[][] SALTO = {{2, 1}, {1, 2}, {-1, 2}, {-2, 1},
{-2, -1}, {-1, -2}, {1, -2}, {2, -1}};
private int x0, y0;
// constructor
public CaballoSaltador(int x, int y) throws Exception {
if ((x < 1) || (x > N)
|| (y < 1) || (y > N)) {
throw new Exception("Coordenadas fuera de rango");
}
x0 = x;
y0 = y;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
tablero[i][j] = 0;
}
}
tablero[x0][y0] = 1;
exito = false;
}
public boolean resolverProblema() {
saltoCaballo(x0, y0, 2);
return exito;
}
private void saltoCaballo(int x, int y, int i) {
int nx, ny;
int k;
k = 0; // inicializa el conjunto de posibles movimientos
do {
k++;
nx = x + SALTO[k - 1][0];
ny = y + SALTO[k - 1][1];
// determina si nuevas coordenadas son aceptables
if ((nx >= 1) && (nx <= N) && (ny >= 1) && (ny <= N)
&& (tablero[nx][ny] == 0)) {
tablero[nx][ny] = i; // anota movimiento
if (i < N * N) {
saltoCaballo(nx, ny, i + 1);
// se analiza si se ha completado la solución
if (!exito) { // no se alcanzó la solución
tablero[nx][ny] = 0; // se borra anotación
}
} else {
exito = true; // tablero cubierto
}
}
} while ((k < 8) && !exito);
}
//muestra por pantalla los pasos del caballo
void escribirTablero() {
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
System.out.print(tablero[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
............................................................................................................................................
Metodo Main
package CaballoSaltador;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
*
* @author SaruraiTensai
*/
public class VueltaAtras {
/**
* @param args the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
boolean solucion;
BufferedReader entrada = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try {
System.out.println("Posicion inicial del caballo. ");
System.out.print(" x = ");
x = Integer.parseInt(entrada.readLine());
System.out.print(" y = ");
y = Integer.parseInt(entrada.readLine());
CaballoSaltador miCaballo = new CaballoSaltador(x, y);
solucion = miCaballo.resolverProblema();
if (solucion) {
miCaballo.escribirTablero();
}
} catch (Exception m) {
System.out.println("No se pudo probar el algoritmo, " + m);
}
}
}
Corrida
Este es el cuadro 8*8, esta enumerada con el numero de salto del caballo hasta recorrer toda la tabla.
Lista doblemente enlazada en java
Generar lista doblemente enlazada
1. con inserción al inicio
2. con inserción al final
3. eliminar un elemento
4. modificar un elemento
5. impresión ascendente y descendente
6. copiar los elemento a una lista simple
1. con inserción al inicio
2. con inserción al final
3. eliminar un elemento
4. modificar un elemento
5. impresión ascendente y descendente
6. copiar los elemento a una lista simple
Código Aquí
package listadoblementeenlazada;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ListaDoblementeEnlazada {
static class Nodo {
int dato;
Nodo ant;
Nodo sig;
}
static class NodoSimple {
int dato;
NodoSimple sig;
}
public static int validarNumero() {
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
int valorNum = 0;
boolean numero = false;
while (!numero) {
try {
String
cadena = leer.nextLine();
valorNum = Integer.parseInt(cadena);
numero = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error,
ingrese un numero");
}
}
return valorNum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Insercion al
incio
System.out.println("Ingrese el multiplo m:");
int m = validarNumero();
System.out.println("Ingrese el tamaño n:");
int n = validarNumero();;
Nodo top = null;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Nodo temp = new Nodo();
temp.dato = i * m;
temp.ant = null;
if (top == null) {
temp.sig = null;
} else {
temp.sig = top;
top.ant = temp;
}
top = temp;
}
System.out.println("Impresion de lista insercion al inicio");
//Impresion ascendente
Nodo temp1 = top;
while (temp1 != null) {
System.out.println("" +
temp1.dato);
temp1 =
temp1.sig;
}
// Insercion al final
Nodo top1 = null;
Nodo ultimo = null;
Nodo temp;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
temp = new Nodo();
temp.dato = i * m;
temp.sig = null;
if (top1 == null) {
temp.ant = null;
top1 = temp;
} else {
ultimo.sig = temp;
temp.ant = ultimo;
}
ultimo = temp;
}
System.out.println("Impresion de lista insercion al final");
//Impresion ascendente
temp1 = top1;
while (temp1 != null) {
System.out.println("" +
temp1.dato);
temp1 =
temp1.sig;
}
System.out.println("Impresion al de lista insercion al inicio ascendente");
//Impresion ascendente
temp1 = top;
while (temp1 != null) {
System.out.println("" +
temp1.dato);
temp1 =
temp1.sig;
}
System.out.println("Impresion al de lista insercion al inicio descendente");
//Impresion desendente
temp1 = top;
while (temp1.sig != null) {
temp1 = temp1.sig;
}
while (temp1 != null) {
System.out.println("" +
temp1.dato);
temp1 =
temp1.ant;
}
System.out.println("Ingrese
el elemento a eliminar:");
//Eliminar
int buscar = validarNumero();
temp1 = top;
while (temp1.dato != buscar
&& temp1.sig!=null) {
temp1 = temp1.sig;
}
if(temp1.sig==null && temp1==null){
System.out.println("No
se encontro el elemento");
}else{
temp1.ant.sig = temp1.sig;
temp1.sig.ant = temp1.ant;
}
System.out.println("Impresion eliminar");
//Impresion ascendente
temp1 = top;
while (temp1 != null) {
System.out.println("" +
temp1.dato);
temp1 =
temp1.sig;
}
System.out.println("Ingrese el elemento a modificar:");
//modificar
buscar = validarNumero();
temp1 = top;
while (temp1.dato != buscar && temp1.sig!=null)
{//temp1.sig==null para que no se haga un bucle infinito
temp1 =
temp1.sig;
}if(temp1.sig==null && temp1==null){
System.out.println("No
se encontro el elemento");
}else{
System.out.println("Ingrese el numero a modificar:");
int modificar = validarNumero();
temp1.dato = modificar;
}
System.out.println("Impresion al modificar");
//Impresion ascendente
temp1 = top;
while (temp1 != null) {
System.out.println("" +
temp1.dato);
temp1 = temp1.sig;
}
//
temp1=top;
NodoSimple top2 =
null;
NodoSimple ultimo1 = null;
NodoSimple temp2;
while(temp1!=null){
//for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
temp2 = new NodoSimple();
temp2.dato = temp1.dato;
temp2.sig = null;
if (top2 == null) {
top2 = temp2;
} else {
ultimo1.sig = temp2;
}
ultimo1 = temp2;
temp1=temp1.sig;
}
System.out.println("Lista doblemente enlazada pasada a lista
simple");
temp2=top2;
while (temp2 != null) {
System.out.println("" +
temp2.dato);
temp2 =
temp2.sig;
}
}
}
Corrida
Traslación de lista simple a arreglo, pila, cola y lista circular en java
Generar una lista
simple con inserción al final, de n elementos y múltiplos de m, luego pasar a:
1) un arreglo, 2) una lista circular, 3) una pila, 4) una cola.
· Código aquí
package
deberTraslacion;
import
java.util.Scanner;
public
class DeberTraslacion {
public static int validarNumero() {
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
int valorNum = 0;
boolean numero = false;
while (!numero) {
try {
String cadena =
leer.nextLine();
valorNum =
Integer.parseInt(cadena);
numero = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error,
ingrese un numero");
}
}
return valorNum;
}
public static
class Nodo {
int dato;
Nodo sig;
}
public static void
main(String[] args) {
boolean salir = false;
int opMenu;
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
//insercion al final
System.out.println("Generación de
una lista simple con inserción al final");
System.out.print("Ingrese n :");
int n =
validarNumero();
System.out.print("Ingrese m
:");
int m = validarNumero();
//genero lista
Nodo top = null;
Nodo ultimo = top;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Nodo temp = new
Nodo();
temp.dato = i * m;
temp.sig = null;
if (top == null) {// primer nodo
top = temp;
} else {
ultimo.sig = temp;
}
ultimo = temp;
}
Nodo temp = top;
System.out.println("Imprimir la lista
simple:");
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print("
"+temp.dato);
temp = temp.sig;
}
System.out.println("");
////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Nodo tempO = top;
String menuTraslacion =
"\nMenu" + "\n Pasar a un:" + "\n 1.Arreglo" +
"\n 2.Lista circular" + "\n 3.Pila" + "\n 4.Cola"
+ "\n 5.Salir";
do {
System.out.println(menuTraslacion);
opMenu = validarNumero();
switch (opMenu) {
case 1: {
tempO = top;
int vec[] = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n;
i++) {
vec[i] = tempO.dato;
tempO = tempO.sig;//por
que tiene que pasar al siguiente elemento
}
System.out.println("La
lista simple pasada a un arreglo es:");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print("
" + vec[i]);
}
System.out.println("");
}
break;
case 2: {
tempO = top;
Nodo top1 = null;
Nodo ultimo1 = top1;
//insertar al inicio de la
lista circular
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Nodo temp1 = new Nodo();
temp1.dato =
tempO.dato;
tempO = tempO.sig;
if (top1 == null) {
temp1.sig = temp1;
ultimo1 = temp1;
} else {
temp1.sig = top1;
ultimo1.sig =
temp1;
}
top1 = temp1;
}
//Para imprimir
System.out.println("La
lista simple pasada a una lista circular es:");
Nodo temp1 = top1;
while (temp1.sig != top1) { //imprime lista
System.out.print("
" + temp1.dato);
temp1 = temp1.sig;
}
System.out.print("
" + temp1.dato);
System.out.println("");
}
break;
case 3: {
tempO = top;
Nodo top2 = null;//Mi top2
sera mi pila de esta opcion
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Nodo temp2 = new Nodo();
temp2.dato =
tempO.dato;
tempO = tempO.sig;
if (top2 == null) {
temp2.sig = null;
} else {
temp2.sig = top2;
}
top2 = temp2;
}
Nodo temp2 = top2;
System.out.println("La
lista simple pasada a una pila es:");
while (temp2 != null) { //imprime lista
System.out.print("
" + temp2.dato);
temp2 = temp2.sig;
}
System.out.println("");
}
break;
case 4: {
tempO = top;
Nodo top3 = tempO; // la
cola es FIFO
//Para imprimir la
cola
Nodo temp3 = top3;
System.out.println("La
lista simple pasada a una cola es:");
while (temp3 != null) {
System.out.print("
" + temp3.dato);
temp3 = temp3.sig;
}
System.out.println("");
}
break;
case 5: {
salir = true;
System.out.println("Fin de ejecucion");
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Error : La opcion no existe... ");
break;
}
} while (!salir);
}
}
Corrida
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)