Código aquí
package ejercicio;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public void quickSort(Vehiculo vector[]) {
int n = vector.length;
quicksort(vector, 0, n - 1);
}
private void quicksort(Vehiculo a[], int primero, int ultimo) {
int i, j, central;
Vehiculo pivote;
central = (primero + ultimo) / 2;
pivote = a[central];
i = primero;
j = ultimo;
do {
while (a[i].compareTo(pivote) < 0) {
i++;
}
while (a[j].compareTo(pivote) > 0) {
j--;
}
if (i <= j) {
Vehiculo aux = a[i]; //intercambio
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = aux;
i++;
j--;
}
} while (i <= j);
if (primero < j) {
quicksort(a, primero, j); // mismo proceso con sublista izqda
}
if (i < ultimo) {
quicksort(a, i, ultimo); // mismo proceso con sublista drcha
}
}
public void listar(Vehiculo arreglo[]) {
int pos = arreglo.length;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
System.out.println((i + 1) + " : " + arreglo[i].toString());
}
System.out.println(".........................................................................");
}
public int busquedaLineal(Vehiculo[] vector, Vehiculo dato) {
int n = vector.length;
int pos = -1;
for (int i = 0; ((i < n) && (pos == -1)); i++) {
if (vector[i].compareTo(dato) == 0) {
pos = i;
}
}
return pos;
}
/**
*
* @param vector
* @param dato
* @return
*/
public int busquedaBinaria(Vehiculo[] vector, Vehiculo dato) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
metodo.quickSort(vector);
int n = vector.length;
int izq = 0;
int der = n - 1;
int centro = (izq + der) / 2;
while ((izq <= der) && (!(vector[centro].compareTo(dato) == 0))) {
if (dato.compareTo(vector[centro]) < 0) {
der = centro - 1;
} else {
izq = centro + 1;
}
centro = (izq + der) / 2;
}
if (izq > der) {
return -1;
} else {
return centro;
}
}
public int busquedaLinealRec(Vehiculo[] vector, Vehiculo dato) {
int n = vector.length;
int i = this.busquedaLinealRecursiva(vector, dato, n - 1, 0);
return i;
}
private int busquedaLinealRecursiva(Vehiculo a[], Vehiculo clave, int n, int i) {
if (i == n + 1) {
return -1;
} else {
if (a[i].compareTo(clave) == 0) {
return i;
} else {
return busquedaLinealRecursiva(a, clave, n, i + 1);
}
}
}
public int busquedaBinariaRec(Vehiculo[] vector, Vehiculo dato) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
metodo.quickSort(vector);
int n = vector.length;
int i = this.busquedaBinariaRecursiva(vector, 0, n - 1, dato);
return i;
}
private int busquedaBinariaRecursiva(Vehiculo vector[], int izq, int der, Vehiculo dato) {
int centro = (izq + der) / 2;
if (izq > der) {
return -1;
} else if (dato.compareTo(vector[centro]) == 0) {
return centro;
} else if (dato.compareTo(vector[centro]) < 0) {
return busquedaBinariaRecursiva(vector, izq, centro - 1, dato);
} else {
return busquedaBinariaRecursiva(vector, centro + 1, der, dato);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
Vehiculo arreglo[] = new Vehiculo[5];
arreglo[0] = new Vehiculo("ada27", 30000D, new Date(112, 10, 12));
arreglo[1] = new Vehiculo("chj5", 27000D, new Date(100, 5, 23));
arreglo[2] = new Vehiculo("cjk77", 40000D, new Date(109, 3, 22));
arreglo[3] = new Vehiculo("bmn90", 35000D, new Date(104, 11, 19));
arreglo[4] = new Vehiculo("asd31", 17000D, new Date(105, 12, 21));
System.out.println("Arreglo con datos");
metodo.listar(arreglo);
Date dato = new Date(104, 11, 19);//podemos validar la fecha revisar entarada antigua
System.out.println("FEcha buscada es "+ dato.toString());
Vehiculo datoVehiculo = new Vehiculo(null, null, dato);
int num;
num = metodo.busquedaLineal(arreglo, datoVehiculo);
// metodo.quickSort(arreglo);
// num = metodo.busquedaLinealRec(arreglo, datoVehiculo);
// num = metodo.busquedaBinaria(arreglo, datoVehiculo);// para que imprima correctamente primero tiene que ordenarlo
// num = metodo.busquedaBinariaRec(arreglo, datoVehiculo);
if(num>0){
System.out.println("El elemneto encontado es "+ arreglo[num].toString());
}else{
System.out.println("Elemento no encontrado");
}
}
}
..........................................................................................................................................................
Clase Vehiculo
package ejercicio;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Vehiculo implements Comparable{
private String placa;
private Double precio;
private Date fechaFabricacion;
public Vehiculo() {
}
public Vehiculo(String placa, Double precio, Date fechaFabricacion) {
this.placa = placa;
this.precio = precio;
this.fechaFabricacion = fechaFabricacion;
}
public String getPlaca() {
return placa;
}
public void setPlaca(String placa) {
this.placa = placa;
}
public void setPrecio(Double precio) {
this.precio = precio;
}
public void setFechaFabricacion(Date fechaFabricacion) {
this.fechaFabricacion = fechaFabricacion;
}
public Double getPrecio() {
return precio;
}
public Date getFechaFabricacion() {
return fechaFabricacion;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
SimpleDateFormat formateador = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
return "{ placa= " + placa + ", precio= " + precio + ", fechaFabricacion=" + formateador.format(fechaFabricacion) + " }";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) { //comparamos String
Vehiculo c = (Vehiculo) o;
int fechaCmp = this.fechaFabricacion.compareTo(c.fechaFabricacion);
return fechaCmp;// aqui solo podemos poner returm placaCmp;
}
}
Captura
JavaYmas
viernes, 14 de agosto de 2015
Métodos de ordenación burbuja, selección, inserción, shellSort, MergeSort y QuickSort con objetos en java
Código Aquí
package ejercicio;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void ordSeleccion(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int indiceMenor, i, j, n;
n = vector.length;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
// comienzo de la exploración en índice i
indiceMenor = i;
// j explora la sublista a[i+1]..a[n-1]
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (vector[j].compareTo(vector[indiceMenor]) < 0) {
indiceMenor = j;
}
}
// sitúa el elemento mas pequeño en a[i]
if (i != indiceMenor) {
Vehiculo aux = vector[i];
vector[i] = vector[indiceMenor];
vector[indiceMenor] = aux;
}
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void ordInsercion(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int n = vector.length;
int i, j;
Vehiculo aux;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
/* indice j es para explorar la sublista a[i-1]..a[0] buscando la
posicion correcta del elemento destino*/
j = i;
aux = vector[i];
// se localiza el punto de inserción explorando hacia abajo
while (j > 0 && (aux.compareTo(vector[j - 1]) < 0)) {
// desplazar elementos hacia arriba para hacer espacio
vector[j] = vector[j - 1];
j--;
}
vector[j] = aux;
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void burbuja(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int n = vector.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) // sitúa mínimo de a[i+1]...a[n-1] en a[i]
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if ((vector[i].compareTo(vector[j])) > 0) {
Vehiculo aux = vector[i];
vector[i] = vector[j];
vector[j] = aux;
}
}
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void shellSort(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int intervalo, i, j, k;
int n = vector.length;
intervalo = n / 2;
while (intervalo > 0) {
for (i = intervalo; i < n; i++) {
j = i - intervalo;
while (j >= 0) {
k = j + intervalo;
if (vector[j].compareTo(vector[k]) <= 0) {
j = -1; // par de elementos ordenado
} else {
Vehiculo aux = vector[j];//intercambio
vector[j] = vector[j + 1];
vector[j + 1] = aux;
j -= intervalo;
}
}
}
intervalo = intervalo / 2;
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void quickSort(Vehiculo vector[]) {
int n = vector.length;
quicksort(vector, 0, n - 1);
}
private void quicksort(Vehiculo a[], int primero, int ultimo) {
int i, j, central;
Vehiculo pivote;
central = (primero + ultimo) / 2;
pivote = a[central];
i = primero;
j = ultimo;
do {
while (a[i].compareTo(pivote) < 0) {
i++;
}
while (a[j].compareTo(pivote) > 0) {
j--;
}
if (i <= j) {
Vehiculo aux = a[i]; //intercambio
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = aux;
i++;
j--;
}
} while (i <= j);
if (primero < j) {
quicksort(a, primero, j); // mismo proceso con sublista izqda
}
if (i < ultimo) {
quicksort(a, i, ultimo); // mismo proceso con sublista drcha
}
}
public void mergeSort(Vehiculo arreglo[]) {
int n = arreglo.length;
Vehiculo tmpArray[] = new Vehiculo[n];
mergeSort(arreglo, tmpArray, 0, n - 1);
}
private void mergeSort(Vehiculo a[], Vehiculo b[], int izq, int der) {
int centro;
if (izq < der) {
centro = (izq + der) / 2;
mergeSort(a, b, izq, centro);
mergeSort(a, b, centro + 1, der);
fusion(a, b, izq, centro + 1, der);
}
}
private void fusion(Vehiculo a[], Vehiculo b[], int izq, int centro, int der) {
int finalIzq, nroelem, tmp;
finalIzq = centro - 1;
tmp = izq;
nroelem = der - izq + 1;
while ((izq <= finalIzq) && (centro <= der)) {
if (a[izq].compareTo(a[centro]) < 0) {
b[tmp] = a[izq];
izq++;
} else {
b[tmp] = a[centro];
centro++;
}
tmp++;
}
while (izq <= finalIzq) {
b[tmp] = a[izq];
tmp++;
izq++;
}
while (centro <= der) {
b[tmp] = a[centro];
tmp++;
centro++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= nroelem; i++) {
a[der] = b[der];
der--;
}
}
public void listar(Vehiculo arreglo[]) {
int pos = arreglo.length;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
System.out.println((i + 1) + " : " + arreglo[i].toString());
}
System.out.println(".........................................................................");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
Vehiculo arreglo[] = new Vehiculo[5];
arreglo[0] = new Vehiculo("ada27", 30000D, new Date(1183282843222L));
arreglo[1] = new Vehiculo("chj5", 27000D, new Date(1090092212322L));
arreglo[2] = new Vehiculo("cjk77", 40000D, new Date(1228998294563L));
arreglo[3] = new Vehiculo("bmn90", 35000D, new Date(1393911139902L));
arreglo[4] = new Vehiculo("asd31", 17000D, new Date(1297484838999L));
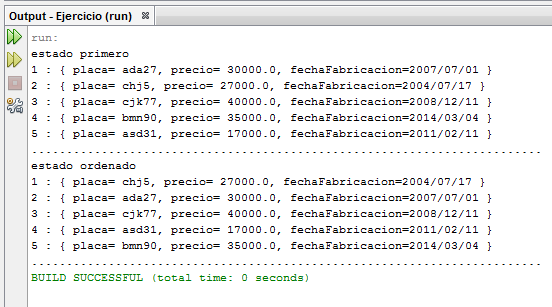
System.out.println("estado primero");
metodo.listar(arreglo);
System.out.println("estado ordenado");
// metodo.burbuja(arreglo);
// metodo.ordInsercion(arreglo);
// metodo.ordSeleccion(arreglo);
// metodo.shellSort(arreglo);
// metodo.mergeSort(arreglo);
metodo.quickSort(arreglo);
metodo.listar(arreglo);
}
}
..........................................................................................................................................................
Clase Vehiculo
package ejercicio;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Vehiculo implements Comparable{
private String placa;
private Double precio;
private Date fechaFabricacion;
public Vehiculo() {
}
public Vehiculo(String placa, Double precio, Date fechaFabricacion) {
this.placa = placa;
this.precio = precio;
this.fechaFabricacion = fechaFabricacion;
}
public String getPlaca() {
return placa;
}
public void setPlaca(String placa) {
this.placa = placa;
}
public void setPrecio(Double precio) {
this.precio = precio;
}
public void setFechaFabricacion(Date fechaFabricacion) {
this.fechaFabricacion = fechaFabricacion;
}
public Double getPrecio() {
return precio;
}
public Date getFechaFabricacion() {
return fechaFabricacion;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
SimpleDateFormat formateador = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
return "{ placa= " + placa + ", precio= " + precio + ", fechaFabricacion=" + formateador.format(fechaFabricacion) + " }";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) { //comparamos String
Vehiculo c = (Vehiculo) o;
int fechaCmp = this.fechaFabricacion.compareTo(c.fechaFabricacion);
return fechaCmp;// aqui solo podemos poner returm placaCmp;
}
}
Captura
package ejercicio;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void ordSeleccion(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int indiceMenor, i, j, n;
n = vector.length;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
// comienzo de la exploración en índice i
indiceMenor = i;
// j explora la sublista a[i+1]..a[n-1]
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (vector[j].compareTo(vector[indiceMenor]) < 0) {
indiceMenor = j;
}
}
// sitúa el elemento mas pequeño en a[i]
if (i != indiceMenor) {
Vehiculo aux = vector[i];
vector[i] = vector[indiceMenor];
vector[indiceMenor] = aux;
}
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void ordInsercion(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int n = vector.length;
int i, j;
Vehiculo aux;
for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
/* indice j es para explorar la sublista a[i-1]..a[0] buscando la
posicion correcta del elemento destino*/
j = i;
aux = vector[i];
// se localiza el punto de inserción explorando hacia abajo
while (j > 0 && (aux.compareTo(vector[j - 1]) < 0)) {
// desplazar elementos hacia arriba para hacer espacio
vector[j] = vector[j - 1];
j--;
}
vector[j] = aux;
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void burbuja(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int n = vector.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) // sitúa mínimo de a[i+1]...a[n-1] en a[i]
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if ((vector[i].compareTo(vector[j])) > 0) {
Vehiculo aux = vector[i];
vector[i] = vector[j];
vector[j] = aux;
}
}
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void shellSort(Vehiculo[] vector) {
int intervalo, i, j, k;
int n = vector.length;
intervalo = n / 2;
while (intervalo > 0) {
for (i = intervalo; i < n; i++) {
j = i - intervalo;
while (j >= 0) {
k = j + intervalo;
if (vector[j].compareTo(vector[k]) <= 0) {
j = -1; // par de elementos ordenado
} else {
Vehiculo aux = vector[j];//intercambio
vector[j] = vector[j + 1];
vector[j + 1] = aux;
j -= intervalo;
}
}
}
intervalo = intervalo / 2;
}
}
/**
*
* @param vector
*
*/
public void quickSort(Vehiculo vector[]) {
int n = vector.length;
quicksort(vector, 0, n - 1);
}
private void quicksort(Vehiculo a[], int primero, int ultimo) {
int i, j, central;
Vehiculo pivote;
central = (primero + ultimo) / 2;
pivote = a[central];
i = primero;
j = ultimo;
do {
while (a[i].compareTo(pivote) < 0) {
i++;
}
while (a[j].compareTo(pivote) > 0) {
j--;
}
if (i <= j) {
Vehiculo aux = a[i]; //intercambio
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = aux;
i++;
j--;
}
} while (i <= j);
if (primero < j) {
quicksort(a, primero, j); // mismo proceso con sublista izqda
}
if (i < ultimo) {
quicksort(a, i, ultimo); // mismo proceso con sublista drcha
}
}
public void mergeSort(Vehiculo arreglo[]) {
int n = arreglo.length;
Vehiculo tmpArray[] = new Vehiculo[n];
mergeSort(arreglo, tmpArray, 0, n - 1);
}
private void mergeSort(Vehiculo a[], Vehiculo b[], int izq, int der) {
int centro;
if (izq < der) {
centro = (izq + der) / 2;
mergeSort(a, b, izq, centro);
mergeSort(a, b, centro + 1, der);
fusion(a, b, izq, centro + 1, der);
}
}
private void fusion(Vehiculo a[], Vehiculo b[], int izq, int centro, int der) {
int finalIzq, nroelem, tmp;
finalIzq = centro - 1;
tmp = izq;
nroelem = der - izq + 1;
while ((izq <= finalIzq) && (centro <= der)) {
if (a[izq].compareTo(a[centro]) < 0) {
b[tmp] = a[izq];
izq++;
} else {
b[tmp] = a[centro];
centro++;
}
tmp++;
}
while (izq <= finalIzq) {
b[tmp] = a[izq];
tmp++;
izq++;
}
while (centro <= der) {
b[tmp] = a[centro];
tmp++;
centro++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= nroelem; i++) {
a[der] = b[der];
der--;
}
}
public void listar(Vehiculo arreglo[]) {
int pos = arreglo.length;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
System.out.println((i + 1) + " : " + arreglo[i].toString());
}
System.out.println(".........................................................................");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
Vehiculo arreglo[] = new Vehiculo[5];
arreglo[0] = new Vehiculo("ada27", 30000D, new Date(1183282843222L));
arreglo[1] = new Vehiculo("chj5", 27000D, new Date(1090092212322L));
arreglo[2] = new Vehiculo("cjk77", 40000D, new Date(1228998294563L));
arreglo[3] = new Vehiculo("bmn90", 35000D, new Date(1393911139902L));
arreglo[4] = new Vehiculo("asd31", 17000D, new Date(1297484838999L));
System.out.println("estado primero");
metodo.listar(arreglo);
System.out.println("estado ordenado");
// metodo.burbuja(arreglo);
// metodo.ordInsercion(arreglo);
// metodo.ordSeleccion(arreglo);
// metodo.shellSort(arreglo);
// metodo.mergeSort(arreglo);
metodo.quickSort(arreglo);
metodo.listar(arreglo);
}
}
..........................................................................................................................................................
Clase Vehiculo
package ejercicio;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Vehiculo implements Comparable{
private String placa;
private Double precio;
private Date fechaFabricacion;
public Vehiculo() {
}
public Vehiculo(String placa, Double precio, Date fechaFabricacion) {
this.placa = placa;
this.precio = precio;
this.fechaFabricacion = fechaFabricacion;
}
public String getPlaca() {
return placa;
}
public void setPlaca(String placa) {
this.placa = placa;
}
public void setPrecio(Double precio) {
this.precio = precio;
}
public void setFechaFabricacion(Date fechaFabricacion) {
this.fechaFabricacion = fechaFabricacion;
}
public Double getPrecio() {
return precio;
}
public Date getFechaFabricacion() {
return fechaFabricacion;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
SimpleDateFormat formateador = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
return "{ placa= " + placa + ", precio= " + precio + ", fechaFabricacion=" + formateador.format(fechaFabricacion) + " }";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) { //comparamos String
Vehiculo c = (Vehiculo) o;
int fechaCmp = this.fechaFabricacion.compareTo(c.fechaFabricacion);
return fechaCmp;// aqui solo podemos poner returm placaCmp;
}
}
Captura
Sudoku en java
Código aquí
package ejercicio;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public static final int DIMENSION = 9; // constante
public void imprimir(int[][] tablero) {
for (int i = 0; i < DIMENSION; i++) {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
System.out.println();
}
for (int j = 0; j < DIMENSION; j++) {
if (j % 3 == 0) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.print(tablero[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public boolean resolver(int[][] tablero) {
for (int i = 0; i < DIMENSION; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < DIMENSION; j++) {
if (tablero[i][j] != 0) {
continue;
}
for (int k = 1; k <= 9; k++) {
if (esPosibleInsertar(tablero, i, j, k)) {
tablero[i][j] = k;
boolean b = resolver(tablero);
if (b) {
return true;
}
tablero[i][j] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
}
System.out.println("Encontrada solución:");
imprimir(tablero);
return true;
}
public boolean esPosibleInsertar(int[][] tablero, int i, int j, int valor) {
//Comprueba columna
for (int a = 0; a < DIMENSION; a++) {
if (a != i && tablero[a][j] == valor) {
return false;
}
}
//Comprueba fila
for (int a = 0; a < DIMENSION; a++) {
if (a != j && tablero[i][a] == valor) {
return false;
}
}
//Comprueba cuadardo
int y = (i / 3) * 3;
int x = (j / 3) * 3;
for (int a = 0; a < DIMENSION / 3; a++) {
for (int b = 0; b < DIMENSION / 3; b++) {
if (a != i && b != j && tablero[y + a][x + b] == valor) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public int[][] generarSudoku() {
int[][] sudok = new int[9][9];
for (int i = 0; i < sudok.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sudok[1].length; j++) {
int ale = (int) (Math.random() * 10);
if (ale == 5) {
sudok[i][j] = (int) (Math.random() * 9) + 1;
} else {
sudok[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
return sudok;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio miSudoku = new Ejercicio();
System.out.println("Sudoku generado");
int[][] sudoku = miSudoku.generarSudoku();
miSudoku.imprimir(sudoku);
System.out.println("Aveces puede demorar por el algoritmo entre 3-15 min");
if (!miSudoku.resolver(sudoku)) {
System.out.println("El Sudoku notiene solución");
}
}
}
Captura
package ejercicio;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public static final int DIMENSION = 9; // constante
public void imprimir(int[][] tablero) {
for (int i = 0; i < DIMENSION; i++) {
if (i % 3 == 0) {
System.out.println();
}
for (int j = 0; j < DIMENSION; j++) {
if (j % 3 == 0) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.print(tablero[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public boolean resolver(int[][] tablero) {
for (int i = 0; i < DIMENSION; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < DIMENSION; j++) {
if (tablero[i][j] != 0) {
continue;
}
for (int k = 1; k <= 9; k++) {
if (esPosibleInsertar(tablero, i, j, k)) {
tablero[i][j] = k;
boolean b = resolver(tablero);
if (b) {
return true;
}
tablero[i][j] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
}
System.out.println("Encontrada solución:");
imprimir(tablero);
return true;
}
public boolean esPosibleInsertar(int[][] tablero, int i, int j, int valor) {
//Comprueba columna
for (int a = 0; a < DIMENSION; a++) {
if (a != i && tablero[a][j] == valor) {
return false;
}
}
//Comprueba fila
for (int a = 0; a < DIMENSION; a++) {
if (a != j && tablero[i][a] == valor) {
return false;
}
}
//Comprueba cuadardo
int y = (i / 3) * 3;
int x = (j / 3) * 3;
for (int a = 0; a < DIMENSION / 3; a++) {
for (int b = 0; b < DIMENSION / 3; b++) {
if (a != i && b != j && tablero[y + a][x + b] == valor) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public int[][] generarSudoku() {
int[][] sudok = new int[9][9];
for (int i = 0; i < sudok.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sudok[1].length; j++) {
int ale = (int) (Math.random() * 10);
if (ale == 5) {
sudok[i][j] = (int) (Math.random() * 9) + 1;
} else {
sudok[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
return sudok;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio miSudoku = new Ejercicio();
System.out.println("Sudoku generado");
int[][] sudoku = miSudoku.generarSudoku();
miSudoku.imprimir(sudoku);
System.out.println("Aveces puede demorar por el algoritmo entre 3-15 min");
if (!miSudoku.resolver(sudoku)) {
System.out.println("El Sudoku notiene solución");
}
}
}
Captura
El método generar sudoku es opcional puedes creas una matriz int de 9*9 y meterle datos.
Laberinto en java
Código aquí
package ejercicio;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public void imprime(char[][] lab) {
for (int i = 0; i < lab.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lab[1].length; j++) {
System.out.print(lab[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public char[][] generarLaberinto() {
int n = (int) (Math.random() * 12) + 3;
int m = (int) (Math.random() * 12) + 3;
char[][] lab = new char[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < lab.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lab[1].length; j++) {
int ale = (int) (Math.random() * 2) + 1;
if (ale == 1) {
lab[i][j] = ' ';
} else {
lab[i][j] = '#';
}
}
}
int inicio1 = (int) (Math.random() * lab.length);
int inicio2 = (int) (Math.random() * lab[1].length);
lab[inicio1][inicio2] = '.';
return lab;
}
public boolean resuelveLab(char[][] lab) {
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < lab.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lab[1].length; j++) {
if (lab[i][j] == '.') {
y = i;
x = j;
}
}
}
return resuelve(lab, x, y);
}
private boolean resuelve(char[][] lab, int x, int y) {
lab[y][x] = '.';
if (x == 0 || y == 0 || x == lab[0].length - 1 || y == lab.length - 1) {
System.out.println("Encontrada soluciOn: ");
imprime(lab);
return true;
}
// Arriba
if (lab[y - 1][x] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x, y - 1);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// abajo
if (lab[y + 1][x] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x, y + 1);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// Izquierda
if (lab[y][x - 1] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x - 1, y);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// Derecha
if (lab[y][x + 1] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x + 1, y);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// Este camino no tiene solucion
lab[y][x] = ' ';
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio laberinto = new Ejercicio();
System.out.println("Laberinto generado: ");
char[][] lab = laberinto.generarLaberinto();
laberinto.imprime(lab);
boolean soluc = laberinto.resuelveLab(lab);
if (soluc == false) {
System.out.println("No se encontro solucion");
}
}
}
package ejercicio;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public void imprime(char[][] lab) {
for (int i = 0; i < lab.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lab[1].length; j++) {
System.out.print(lab[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public char[][] generarLaberinto() {
int n = (int) (Math.random() * 12) + 3;
int m = (int) (Math.random() * 12) + 3;
char[][] lab = new char[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < lab.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lab[1].length; j++) {
int ale = (int) (Math.random() * 2) + 1;
if (ale == 1) {
lab[i][j] = ' ';
} else {
lab[i][j] = '#';
}
}
}
int inicio1 = (int) (Math.random() * lab.length);
int inicio2 = (int) (Math.random() * lab[1].length);
lab[inicio1][inicio2] = '.';
return lab;
}
public boolean resuelveLab(char[][] lab) {
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < lab.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < lab[1].length; j++) {
if (lab[i][j] == '.') {
y = i;
x = j;
}
}
}
return resuelve(lab, x, y);
}
private boolean resuelve(char[][] lab, int x, int y) {
lab[y][x] = '.';
if (x == 0 || y == 0 || x == lab[0].length - 1 || y == lab.length - 1) {
System.out.println("Encontrada soluciOn: ");
imprime(lab);
return true;
}
// Arriba
if (lab[y - 1][x] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x, y - 1);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// abajo
if (lab[y + 1][x] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x, y + 1);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// Izquierda
if (lab[y][x - 1] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x - 1, y);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// Derecha
if (lab[y][x + 1] == ' ') {
boolean tmp = resuelve(lab, x + 1, y);
if (tmp == true) {
return true;
}
}
// Este camino no tiene solucion
lab[y][x] = ' ';
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio laberinto = new Ejercicio();
System.out.println("Laberinto generado: ");
char[][] lab = laberinto.generarLaberinto();
laberinto.imprime(lab);
boolean soluc = laberinto.resuelveLab(lab);
if (soluc == false) {
System.out.println("No se encontro solucion");
}
}
}
Captura
El punto indica donde comienza para encontrar una salida, el método generar laberinto es opcional puedes tu mandar tu matriz chart de cualquier tamaño.
Validar int , double y Date en java
Código aquí
package ejercicio;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public Integer validarInt() {
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean esEntero = false;
int num = -1;
do {
String cadena = leer.nextLine();
try {
num = Integer.parseInt(cadena);
esEntero = true;
} catch (NumberFormatException nfe) {
System.out.println("Escriba un numero");
}
} while (!esEntero);
return num;
}
public Double validarDouble() {
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean esDouble = false;
double num = -1;
do {
String cadena = leer.nextLine();
try {
num = Double.parseDouble(cadena);
esDouble = true;
} catch (NumberFormatException nfe) {
System.out.println("Escriba un numero");
}
} while (!esDouble);
return num;
}
public Date validarFecha() {
SimpleDateFormat formatoDelTexto = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean esFormato = false;
Date fecha = new Date(0);
do {
String cadena = leer.nextLine();
try {
fecha = formatoDelTexto.parse(cadena);
System.out.println("La fecha que ingreso es " + formatoDelTexto.format(fecha));
esFormato = true;
} catch (ParseException ex) {
// ex.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Escriba la fecha cn el formato yyyy/MM/dd");
}
} while (!esFormato);
return fecha;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
int datoInt = metodo.validarInt();
System.out.println("El numero leido es " + datoInt);
double datoDouble = metodo.validarDouble();
System.out.println("El numero leido es " + datoDouble);
Date datoDate = metodo.validarFecha();
System.out.println("La fecha leida es " + datoDate.toString());
}
}
package ejercicio;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public Integer validarInt() {
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean esEntero = false;
int num = -1;
do {
String cadena = leer.nextLine();
try {
num = Integer.parseInt(cadena);
esEntero = true;
} catch (NumberFormatException nfe) {
System.out.println("Escriba un numero");
}
} while (!esEntero);
return num;
}
public Double validarDouble() {
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean esDouble = false;
double num = -1;
do {
String cadena = leer.nextLine();
try {
num = Double.parseDouble(cadena);
esDouble = true;
} catch (NumberFormatException nfe) {
System.out.println("Escriba un numero");
}
} while (!esDouble);
return num;
}
public Date validarFecha() {
SimpleDateFormat formatoDelTexto = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean esFormato = false;
Date fecha = new Date(0);
do {
String cadena = leer.nextLine();
try {
fecha = formatoDelTexto.parse(cadena);
System.out.println("La fecha que ingreso es " + formatoDelTexto.format(fecha));
esFormato = true;
} catch (ParseException ex) {
// ex.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Escriba la fecha cn el formato yyyy/MM/dd");
}
} while (!esFormato);
return fecha;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
int datoInt = metodo.validarInt();
System.out.println("El numero leido es " + datoInt);
double datoDouble = metodo.validarDouble();
System.out.println("El numero leido es " + datoDouble);
Date datoDate = metodo.validarFecha();
System.out.println("La fecha leida es " + datoDate.toString());
}
}
Captura
Cambio de monedas en java
Código aquí
package ejercicio;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public boolean calcular(int monto, int[] valor, int[] num) {
int cont = dineroTotal(valor, num);
if (cont >= monto) {
int[] cambio = this.cambio(monto, valor, num);
for (int i = 0; i < cambio.length; i++) {
System.out.println(valor[i] + " = " + cambio[i] + " unidad(es)");
}
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
private int[] cambio(int monto, int[] valor, int[] num) {
int[] moneda = new int[valor.length];
for (int i = 0; i < valor.length; i++) {
while (valor[i] <= monto && num[i] > 0) {
moneda[i]++;
num[i]--;
monto = monto - valor[i];
}
}
return moneda;
}
public int dineroTotal(int[] valor, int[] num) {
int cont = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
cont += num[i] * valor[i];
}
return cont;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] moneda = {100, 50, 10, 5, 1};// monedad
int[] cantidadMoneda = {((int) (Math.random() * 100)), (int) (Math.random() * 200),
(int) (Math.random() * 400), (int) (Math.random() * 600), (int) (Math.random() * 1000)};//cantidad de monedas aleatorias
//Quiero en monedas
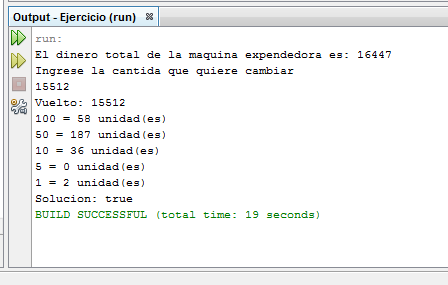
System.out.println("El dinero total de la maquina expendedora es: " + metodo.dineroTotal(moneda, cantidadMoneda));
System.out.println("Ingrese la cantida que quiere cambiar ");
int saldo = leer.nextInt();
System.out.println("Vuelto: " + saldo);
boolean exito = metodo.calcular(saldo, moneda, cantidadMoneda);
System.out.println("Solucion: " + exito);
}
}
package ejercicio;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author Sarurai
*/
public class Ejercicio {
public boolean calcular(int monto, int[] valor, int[] num) {
int cont = dineroTotal(valor, num);
if (cont >= monto) {
int[] cambio = this.cambio(monto, valor, num);
for (int i = 0; i < cambio.length; i++) {
System.out.println(valor[i] + " = " + cambio[i] + " unidad(es)");
}
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
private int[] cambio(int monto, int[] valor, int[] num) {
int[] moneda = new int[valor.length];
for (int i = 0; i < valor.length; i++) {
while (valor[i] <= monto && num[i] > 0) {
moneda[i]++;
num[i]--;
monto = monto - valor[i];
}
}
return moneda;
}
public int dineroTotal(int[] valor, int[] num) {
int cont = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
cont += num[i] * valor[i];
}
return cont;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ejercicio metodo = new Ejercicio();
Scanner leer = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] moneda = {100, 50, 10, 5, 1};// monedad
int[] cantidadMoneda = {((int) (Math.random() * 100)), (int) (Math.random() * 200),
(int) (Math.random() * 400), (int) (Math.random() * 600), (int) (Math.random() * 1000)};//cantidad de monedas aleatorias
//Quiero en monedas
System.out.println("El dinero total de la maquina expendedora es: " + metodo.dineroTotal(moneda, cantidadMoneda));
System.out.println("Ingrese la cantida que quiere cambiar ");
int saldo = leer.nextInt();
System.out.println("Vuelto: " + saldo);
boolean exito = metodo.calcular(saldo, moneda, cantidadMoneda);
System.out.println("Solucion: " + exito);
}
}
Corrida
jueves, 13 de agosto de 2015
El salto del caballo en java , backtracking
Codigo aqui
Clase CaballoSaltador
*
* To change this license header, choose License Headers in Project Properties.
* To change this template file, choose Tools | Templates
* and open the template in the editor.
*/
package CaballoSaltador;
/**
*
* @author SaruraiTensai
*/
public class CaballoSaltador {
static final int N = 8;
static final int n = (N + 1);
private int[][] tablero = new int[n][n];
private boolean exito;
private int[][] SALTO = {{2, 1}, {1, 2}, {-1, 2}, {-2, 1},
{-2, -1}, {-1, -2}, {1, -2}, {2, -1}};
private int x0, y0;
// constructor
public CaballoSaltador(int x, int y) throws Exception {
if ((x < 1) || (x > N)
|| (y < 1) || (y > N)) {
throw new Exception("Coordenadas fuera de rango");
}
x0 = x;
y0 = y;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
tablero[i][j] = 0;
}
}
tablero[x0][y0] = 1;
exito = false;
}
public boolean resolverProblema() {
saltoCaballo(x0, y0, 2);
return exito;
}
private void saltoCaballo(int x, int y, int i) {
int nx, ny;
int k;
k = 0; // inicializa el conjunto de posibles movimientos
do {
k++;
nx = x + SALTO[k - 1][0];
ny = y + SALTO[k - 1][1];
// determina si nuevas coordenadas son aceptables
if ((nx >= 1) && (nx <= N) && (ny >= 1) && (ny <= N)
&& (tablero[nx][ny] == 0)) {
tablero[nx][ny] = i; // anota movimiento
if (i < N * N) {
saltoCaballo(nx, ny, i + 1);
// se analiza si se ha completado la solución
if (!exito) { // no se alcanzó la solución
tablero[nx][ny] = 0; // se borra anotación
}
} else {
exito = true; // tablero cubierto
}
}
} while ((k < 8) && !exito);
}
//muestra por pantalla los pasos del caballo
void escribirTablero() {
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
System.out.print(tablero[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Clase CaballoSaltador
*
* To change this license header, choose License Headers in Project Properties.
* To change this template file, choose Tools | Templates
* and open the template in the editor.
*/
package CaballoSaltador;
/**
*
* @author SaruraiTensai
*/
public class CaballoSaltador {
static final int N = 8;
static final int n = (N + 1);
private int[][] tablero = new int[n][n];
private boolean exito;
private int[][] SALTO = {{2, 1}, {1, 2}, {-1, 2}, {-2, 1},
{-2, -1}, {-1, -2}, {1, -2}, {2, -1}};
private int x0, y0;
// constructor
public CaballoSaltador(int x, int y) throws Exception {
if ((x < 1) || (x > N)
|| (y < 1) || (y > N)) {
throw new Exception("Coordenadas fuera de rango");
}
x0 = x;
y0 = y;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
tablero[i][j] = 0;
}
}
tablero[x0][y0] = 1;
exito = false;
}
public boolean resolverProblema() {
saltoCaballo(x0, y0, 2);
return exito;
}
private void saltoCaballo(int x, int y, int i) {
int nx, ny;
int k;
k = 0; // inicializa el conjunto de posibles movimientos
do {
k++;
nx = x + SALTO[k - 1][0];
ny = y + SALTO[k - 1][1];
// determina si nuevas coordenadas son aceptables
if ((nx >= 1) && (nx <= N) && (ny >= 1) && (ny <= N)
&& (tablero[nx][ny] == 0)) {
tablero[nx][ny] = i; // anota movimiento
if (i < N * N) {
saltoCaballo(nx, ny, i + 1);
// se analiza si se ha completado la solución
if (!exito) { // no se alcanzó la solución
tablero[nx][ny] = 0; // se borra anotación
}
} else {
exito = true; // tablero cubierto
}
}
} while ((k < 8) && !exito);
}
//muestra por pantalla los pasos del caballo
void escribirTablero() {
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
System.out.print(tablero[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
............................................................................................................................................
Metodo Main
package CaballoSaltador;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
*
* @author SaruraiTensai
*/
public class VueltaAtras {
/**
* @param args the command line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
boolean solucion;
BufferedReader entrada = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try {
System.out.println("Posicion inicial del caballo. ");
System.out.print(" x = ");
x = Integer.parseInt(entrada.readLine());
System.out.print(" y = ");
y = Integer.parseInt(entrada.readLine());
CaballoSaltador miCaballo = new CaballoSaltador(x, y);
solucion = miCaballo.resolverProblema();
if (solucion) {
miCaballo.escribirTablero();
}
} catch (Exception m) {
System.out.println("No se pudo probar el algoritmo, " + m);
}
}
}
Corrida
Este es el cuadro 8*8, esta enumerada con el numero de salto del caballo hasta recorrer toda la tabla.
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)